A brief look at water turbines
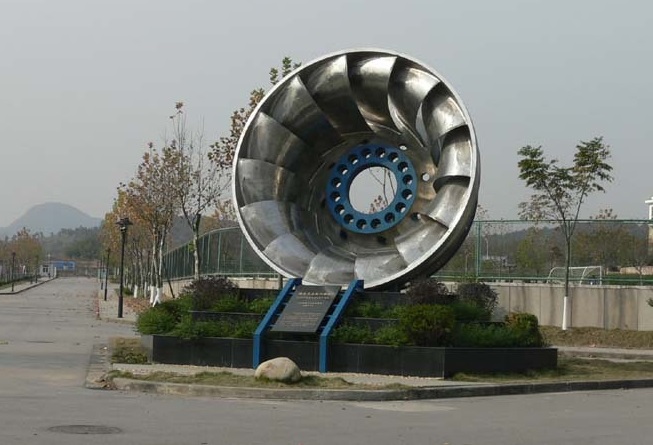
A water turbine is a power machine that converts the energy of water flow into rotating mechanical energy. It belongs to the turbomachinery in fluid machinery. As early as around 100 BC, the embryonic form of water turbines, water wheels, appeared in China, used to lift irrigation and drive grain processing equipment. Modern hydraulic turbines are mostly installed in hydropower stations to drive generators to generate electricity. In a hydropower station, the water in the upstream reservoir is led to the turbine through the diversion pipe, which drives the turbine runner to rotate and drives the generator to generate electricity. The finished water is discharged downstream through the tailpipe. The higher the water head and the greater the flow, the greater the output power of the turbine.
According to the working principle, hydraulic turbines can be divided into two categories: impulse turbines and counterattack turbines. The runner of the impulse turbine is impacted by the water flow and rotates. During the working process, the pressure of the water flow is unchanged, mainly due to the conversion of kinetic energy; the runner of the impact turbine is rotated in the water by the reaction force of the water flow, and the pressure of the water flow during the working process Both energy and kinetic energy have changed, but mainly the conversion of pressure energy.